Question
Investigate the nature of critical points for the given functions:
a) ![]()
b) ![]()
Solution
==================================================================================================
a) 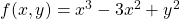
Step-1: Find critical points:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Thus, (2, 0) is the critical point for f(x, y).
Step-2: Find Eigenvalues at critical point:
Hessian matrix of f,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ Hf(x,y) = \begin{vmatrix} \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x^2} & \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x \partial y} \\ \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x \partial y} & \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial y^2} \end{vmatrix} = \begin{vmatrix} 6x-6 & 0\\ 0 & 2 \end{vmatrix} \]](https://ehanghalib.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-156b5ecb5087b9030bd6ce5f5f07512e_l3.png)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Step-3: Find nature of the critical point:
Since eigenvalues of Hf(2,0) are positive, (2, 0) is a local minimum.
==================================================================================================
b) 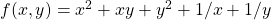
Step-1: Find critical points:
(1) ![]()
(2) ![]()
(3) ![]()
(4) ![]()
Similarly,
(5) ![]()
(6) ![]()
![]()
(7) ![]()
(7) in (1) ![]()
![]()
![]()
From (7), we get ![]()
Thus, ![]() is the critical point for f(x, y).
is the critical point for f(x, y).
Step-2: Find Eigenvalues at critical point:
Hessian matrix of f, Hf(x,y)=∣∣∣∂2f/∂x2∂2f/∂x∂y∂2f/∂x∂y∂2f/∂y2∣∣∣ = ∣∣∣x+3/x311y+3/y3∣∣∣
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ Hf(x,y) = \begin{vmatrix} \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x^2} & \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x \partial y} \\ \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial x \partial y} & \frac{\partial^2 f}{\partial y^2} \end{vmatrix} = \begin{vmatrix} x+3/x^3 & 1\\ 1 & y+3/y^3 \end{vmatrix} \]](https://ehanghalib.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3b058e639f9da9fc20422fe4dbc64d40_l3.png)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Step-3: Find nature of the critical point:
Since eigenvalues of ![]() are positive,
are positive, ![]() is a local minimum.
is a local minimum.